Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 , Zr, and stainless steel and leaching behavior of the fission products and matrix elements
, Zr, and stainless steel and leaching behavior of the fission products and matrix elementsTonna, Ryutaro*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kodama, Yuji*; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kumagai, Yuta; Kusaka, Ryoji; Watanabe, Masayuki
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 55(4), p.1300 - 1309, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:68.31(Nuclear Science & Technology)Simulated debris was synthesized using UO , Zr, and stainless steel and a heat treatment method under inert or oxidizing conditions. The primary U solid phase of the debris synthesized at 1473 K under inert conditions was UO
, Zr, and stainless steel and a heat treatment method under inert or oxidizing conditions. The primary U solid phase of the debris synthesized at 1473 K under inert conditions was UO , whereas a (U,Zr)O
, whereas a (U,Zr)O solid solution formed at 1873 K. Under oxidizing conditions, a mixture of U
solid solution formed at 1873 K. Under oxidizing conditions, a mixture of U O
O and (Fe,Cr)UO
and (Fe,Cr)UO phases formed at 1473 K whereas a (U,Zr)O
phases formed at 1473 K whereas a (U,Zr)O solid solution formed at 1873 K. The leaching behavior of the fission products from the simulated debris was evaluated using two methods: the irradiation method, for which fission products were produced via neutron irradiation, and the doping method, for which trace amounts of non-radioactive elements were doped into the debris. The dissolution behavior of U depended on the properties of the debris and aqueous medium the debris was immersed in. Cs, Sr, and Ba leached out regardless of the primary solid phases. The leaching of high-valence Eu and Ru ions was suppressed, possibly owing to their solid-solution reaction with or incorporation into the uranium compounds of the simulated debris.
solid solution formed at 1873 K. The leaching behavior of the fission products from the simulated debris was evaluated using two methods: the irradiation method, for which fission products were produced via neutron irradiation, and the doping method, for which trace amounts of non-radioactive elements were doped into the debris. The dissolution behavior of U depended on the properties of the debris and aqueous medium the debris was immersed in. Cs, Sr, and Ba leached out regardless of the primary solid phases. The leaching of high-valence Eu and Ru ions was suppressed, possibly owing to their solid-solution reaction with or incorporation into the uranium compounds of the simulated debris.
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Harada, Makoto; Takano, Masahide
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 44(2), p.61 - 64, 2019/04
We performed three-dimensional observation of simulated fuel debris using Synchrotron Computed Tomography (CT). CT was used to make the inside of fuel debris clear. The CT observation provides that a clear contrast in the zirconia rich part and concrete rich part. Zirconia heavier than concrete moved to the lower part when crystals precipitate and aggregates near the bottom surface. As a result, phase separation occurs. The phase separation is caused by the difference in the composition ratio of zirconia, and can also be observed difference in crystal growth mode by composition ratio.
 as simulated corium debris
as simulated corium debrisMorimoto, Kyoichi; Hirooka, Shun; Akashi, Masatoshi; Watanabe, Masashi
no journal, ,
The influence of Gd on characteristics of debris is important for removing the debris from the reactors of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant because subassemblies of nuclear fuels containing Gd O
O were loaded in the some reactor cores. Additionally, it is important to assess the distribution state of Gd from the anxiety of re-criticality caused by the relocation of debris while removing them. In this study, sintered pellets of (U
were loaded in the some reactor cores. Additionally, it is important to assess the distribution state of Gd from the anxiety of re-criticality caused by the relocation of debris while removing them. In this study, sintered pellets of (U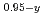 Gd
Gd Zr
Zr )O
)O (y=0,0.5, 2-x=1.989-2.000) were melted and solidified to prepare specimens of simulated corium debris. Phase states and fundamental properties of them were evaluated.
(y=0,0.5, 2-x=1.989-2.000) were melted and solidified to prepare specimens of simulated corium debris. Phase states and fundamental properties of them were evaluated.